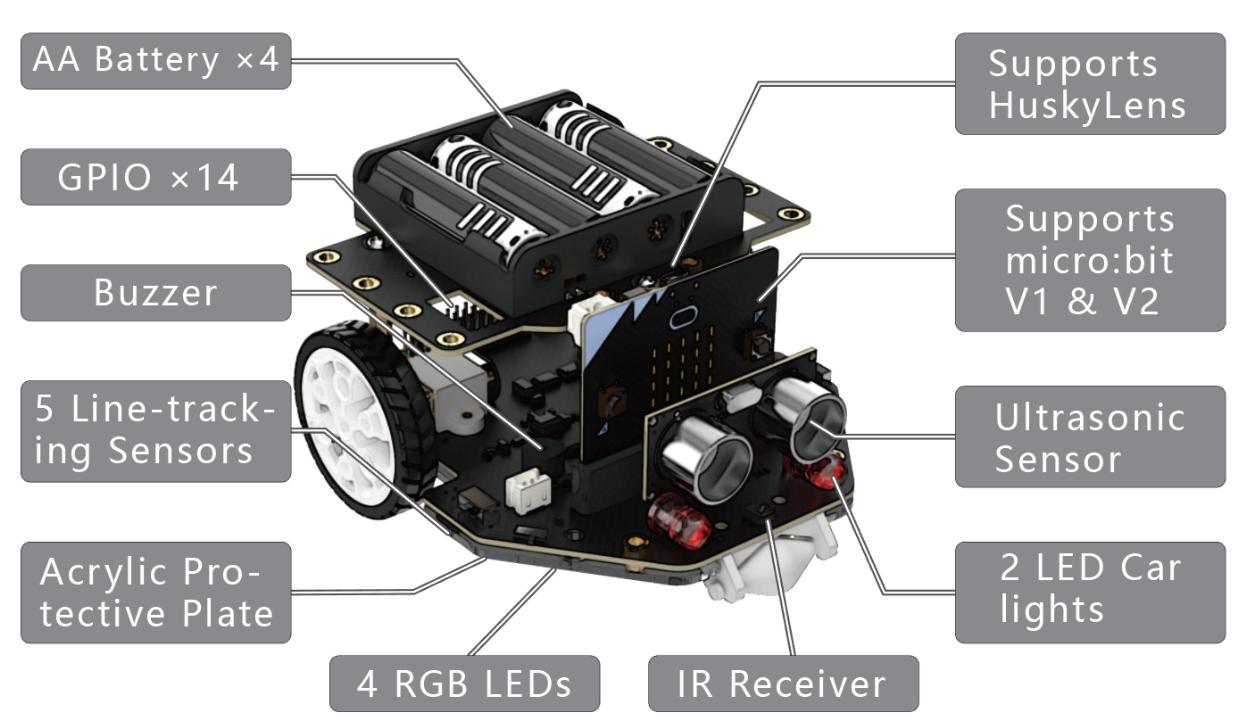
Maqueen Plus V2.0
Eine Bibliothek zum Steuern und Auslesen von Sensordaten beim Maqueen Plus V2.0 mit Micro:bit und MicroPython.
Installation
Auf https://python.microbit.org/v/3 finden Sie eine Online-IDE für MicroPython auf dem Micro:bit.
Kopieren Sie die Datei maqueen.py in den Projektordner, sie kann dann direkt importiert und verwendet werden.
main.py
from microbit import *
from maqueen import *
motor_run(Motor.LEFT, 100)
sleep(1000)
motor_run(Motor.ALL, 100)
sleep(1000)
motor_stop(Motor.ALL)
Bibliothek
maqueen.py
'''
Version: 2.0.2
@see https://github.com/DFRobot/pxt-DFRobot_MaqueenPlus_v20/blob/master/maqueenPlusV2.ts
'''
from micropython import const
from microbit import i2c, display, Image, pin13, pin14, pin15, accelerometer, compass
from machine import time_pulse_us
from neopixel import NeoPixel
from time import sleep_ms, sleep_us, ticks_us
from math import sqrt, asin, cos, sin, atan2, pi
class Motor:
LEFT = 0
RIGHT = 1
ALL = 2
class Direction:
FORWARD = 0
BACKWARD = 1
class Led:
LEFT = 0
RIGHT = 1
ALL = 2
class LineSensor:
L1 = 0
M = 1
R1 = 2
L2 = 3
R2 = 4
class Color:
RED = 0xFF0000
ORANGE = 0xFFA500
YELLOW = 0xFFFF00
GREEN = 0x00FF00
BLUE = 0x0000FF
INDIGO = 0x4B0082
VIOLET = 0x8A2BE2
PURPLE = 0xFF00FF
WHITE = 0xFFFFFF
BLACK = 0x000000
class ColorLED:
L1 = 0
L2 = 1
R2 = 2
R1 = 3
ALL = 4
I2C_ADDR = const(0x10)
ADC0_REGISTER = const(0X1E)
ADC1_REGISTER = const(0X20)
ADC2_REGISTER = const(0X22)
ADC3_REGISTER = const(0X24)
ADC4_REGISTER = const(0X26)
LEFT_LED_REGISTER = const(0X0B)
RIGHT_LED_REGISTER = const(0X0C)
LEFT_MOTOR_REGISTER = const(0X00)
RIGHT_MOTOR_REGISTER = const(0X02)
LINE_STATE_REGISTER = const(0X1D)
VERSION_CNT_REGISTER = const(0X32)
VERSION_DATA_REGISTER = const(0X33)
_neo_pixel = NeoPixel(pin15, 4)
_brightness = 0xff
_heading_window_size = 1
_heading_buffer = [0.0]
_heading_buffer_index = 0
_motor_calibration = [[], []]
def I2CInit():
version_v = 0
i2c.write(I2C_ADDR, bytearray([VERSION_CNT_REGISTER]))
version_v = i2c.read(I2C_ADDR, 1) # read 1 byte
while not version_v:
display.show(Image('90009:09090:00900:09090:90009'))
sleep_ms(500)
display.clear()
i2c.write(I2C_ADDR, bytearray([VERSION_CNT_REGISTER]))
version_v = i2c.read(I2C_ADDR, 1) # read 1 byte
display.show(Image('00000:00009:00090:90900:09000'))
sleep_ms(500)
display.clear()
def motor_calibration(motor: int, speed_factors: list):
'''
Maqueen robots tend to have different motor speeds.
You can provide factors for different speeds to inter/extrapolate
new speeds.
```
motor_calibration(Motor.Right, [(20, 1.28), (200, 1.22)])
```
'''
if motor > 1:
print('No motor index', motor, 'found. Calibration is ignored')
return
_motor_calibration[motor] = sorted(speed_factors, key=lambda x: x[0])
def motor_get_calibration(motor: int):
'''
Returns a copy of the calibration data for the given motor.
```
motor_get_calibration(Motor.RIGHT) # => [(20, 1.28), (200, 1.22)]
```
'''
return [s for s in _motor_calibration[motor]]
def _get_speed(motor: int, speed: int):
num_calibs = len(_motor_calibration[motor])
if motor > 1 or num_calibs == 0:
return speed
elif num_calibs == 1:
return int(_motor_calibration[motor][0][1] * speed)
elif num_calibs == 2:
calibs = _motor_calibration[motor]
x1 = calibs[0][0]
y1 = calibs[0][1]
x2 = calibs[1][0]
y2 = calibs[1][1]
m = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1)
factor = y1 + (speed - x1) * m
return int(factor * speed)
else:
calibs = _motor_calibration[motor]
bigger = [x for x in calibs if x[0] > speed]
if len(bigger) > 0:
cal2 = bigger[0]
else:
cal2 = calibs[-1]
idx_cal2 = calibs.index(cal2)
if idx_cal2 > 0:
cal1 = calibs[idx_cal2 - 1]
else:
cal1 = cal2
cal2 = calibs[idx_cal2 + 1]
x1 = cal1[0]
y1 = cal1[1]
x2 = cal2[0]
y2 = cal2[1]
m = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1)
factor = y1 + (speed - x1) * m
return int(factor * speed)
def motor_run(motor: int, speed: int, dir: int = Direction.FORWARD):
'''
Run the motor on the given speed.
speed: 0-255
```
motor_run(Motor.ALL, speed=100, dir=Direction.Forward)
```
'''
if speed < 0:
speed = -speed
dir = Direction.FORWARD if dir == Direction.BACKWARD else Direction.BACKWARD
if motor == Motor.LEFT:
i2c.write(I2C_ADDR, bytearray([LEFT_MOTOR_REGISTER, dir, _get_speed(motor, speed)]))
elif motor == Motor.RIGHT:
i2c.write(I2C_ADDR, bytearray([RIGHT_MOTOR_REGISTER, dir, _get_speed(motor, speed)]))
else:
i2c.write(I2C_ADDR, bytearray([LEFT_MOTOR_REGISTER, dir, _get_speed(Motor.LEFT, speed), dir, _get_speed(Motor.RIGHT, speed)]))
def motor_stop(motor: int = Motor.ALL):
'''
Stop the motor.
```
motor_stop() # => stop both motors
motor_stop(Motor.LEFT) # => stop the left motor
```
'''
motor_run(motor, 0, 0)
def led_red(on: bool, led: int = Led.ALL):
'''
Control the LED.
```
led_red(True) # => turn on both red LED's
led_red(False, Led.LEFT) # => turn off the left red LED
```
'''
if led == Led.LEFT:
i2c.write(I2C_ADDR, bytearray([LEFT_LED_REGISTER, 1 if on else 0]))
elif led == Led.RIGHT:
i2c.write(I2C_ADDR, bytearray([RIGHT_LED_REGISTER, 1 if on else 0]))
else:
switch = 1 if on else 0
i2c.write(I2C_ADDR, bytearray([LEFT_LED_REGISTER, switch, switch]))
def line_sensor(sensor: int):
'''
Read the line sensor.
```
line_sensor(LineSensor.SENSOR_L1) # => 0 or 1
```
'''
i2c.write(I2C_ADDR, bytearray([LINE_STATE_REGISTER]))
data = i2c.read(I2C_ADDR, 1)
if sensor == LineSensor.L2:
return 1 if (data[0] & 0x10) == 0x10 else 0
elif sensor == LineSensor.L1:
return 1 if (data[0] & 0x08) == 0x08 else 0
elif sensor == LineSensor.M:
return 1 if (data[0] & 0x04) == 0x04 else 0
elif sensor == LineSensor.R1:
return 1 if (data[0] & 0x02) == 0x02 else 0
elif sensor == LineSensor.R2:
return 1 if (data[0] & 0x01) == 0x01 else 0
def line_sensor_all():
'''
Read all line sensors at once.
```
line_sensor_all()
# => (left2, left1, middle, right1, right2) # => list[0 or 1]
```
'''
i2c.write(I2C_ADDR, bytearray([LINE_STATE_REGISTER]))
data = i2c.read(I2C_ADDR, 1)
return (
1 if (data[0] & 0x10) == 0x10 else 0,
1 if (data[0] & 0x08) == 0x08 else 0,
1 if (data[0] & 0x04) == 0x04 else 0,
1 if (data[0] & 0x02) == 0x02 else 0,
1 if (data[0] & 0x01) == 0x01 else 0
)
def line_sensor_data(sensor: int) -> int:
'''
Read the raw values of the line sensor.
```
line_sensor_data(LineSensor.L1) # => int
```
'''
i2c.write(I2C_ADDR, bytearray([LINE_STATE_REGISTER]))
if sensor == LineSensor.L2:
i2c.write(I2C_ADDR, bytearray([ADC0_REGISTER]))
buffer = i2c.read(I2C_ADDR, 2)
return buffer[1] << 8 | buffer[0]
if sensor == LineSensor.L1:
i2c.write(I2C_ADDR, bytearray([ADC1_REGISTER]))
buffer = i2c.read(I2C_ADDR, 2)
return buffer[1] << 8 | buffer[0]
elif sensor == LineSensor.M:
i2c.write(I2C_ADDR, bytearray([ADC2_REGISTER]))
buffer = i2c.read(I2C_ADDR, 2)
return buffer[1] << 8 | buffer[0]
elif sensor == LineSensor.R1:
i2c.write(I2C_ADDR, bytearray([ADC3_REGISTER]))
buffer = i2c.read(I2C_ADDR, 2)
return buffer[1] << 8 | buffer[0]
elif sensor == LineSensor.R2:
i2c.write(I2C_ADDR, bytearray([ADC4_REGISTER]))
buffer = i2c.read(I2C_ADDR, 2)
return buffer[1] << 8 | buffer[0]
return 0
def line_sensor_data_all():
'''
Reads the raw values of all the line sensors.
```
line_sensor_data_all()
# => (left2, left1, middle, right1, right2) # => tuple[int]
```
'''
return (
line_sensor_data(LineSensor.L2),
line_sensor_data(LineSensor.L1),
line_sensor_data(LineSensor.M),
line_sensor_data(LineSensor.R1),
line_sensor_data(LineSensor.R2)
)
_last_distance_cm = 100_000 # 1km = 100'000cm
_last_echo_time = ticks_us()
def ultrasonic(trig = pin13, echo = pin14, cache_duration = 500_000) -> int:
'''
Read the ultrasonic sensor. Result is the distance to next obstacle in cm.
If an error (timeout) occurs during the measurement, a distance of 100'000cm = 1km is returned.
After a call to ultrasonic() a pause of at least 20ms should be taken, before another call is made.
```
ultrasonic()
```
'''
global _last_distance_cm, _last_echo_time
# send trigger impuls to ultrasonic sensor
trig.write_digital(1)
sleep_us(10)
trig.write_digital(0)
# measure time to echo, timeout 0.1 s = 100'000 us ≙ 34 m
time_to_echo = time_pulse_us(echo, 1, 100_000)
dt = ticks_us() - _last_echo_time
# if timeout while measuring -> return last measurement or 1km = 100'000cm
if time_to_echo < 0:
# if the last measurement was less than <cache_duration> ago, return the last measurement
if dt < cache_duration:
return _last_distance_cm
return 100_000 # 1km = 100'000cm
else:
_last_echo_time = ticks_us()
# Speed of sound: 340m/s = 34cm/ms = 0.034cm/us
# distance = time_to_echo / 2 * speed of sound
distance = time_to_echo / 2 * 0.034
# distances larger than 4m are limited to 4m (upper range of sensor)
if distance > 400:
_last_distance_cm = 400
else:
_last_distance_cm = round(distance)
return _last_distance_cm
def version():
'''
Read the version of the board.
```
version() # => string like 'MBT0021-EN-2.1'
```
'''
i2c.write(I2C_ADDR, bytearray([VERSION_CNT_REGISTER]))
bytes_to_read = int(i2c.read(I2C_ADDR, 1)[0])
i2c.write(I2C_ADDR, bytearray([VERSION_DATA_REGISTER]))
version = i2c.read(I2C_ADDR, bytes_to_read)
return version.decode('utf-8')
def rgb(r: int, g: int, b: int):
'''
Convert RGB to int. This can be used to set the color of the color LED.
r, g, b: 0-255
```
led_rgb(rgb(255, 0, 0)) # => red
```
'''
return (r << 16) | (g << 8) | b
def hsl(h: int, s: int, l: int):
'''
Convert HSL to int. This can be used to set the color of the color LED.
h: 0-360, s, l: 0-100
```
led_rgb(hsl(0, 100, 50)) # => red
led_rgb(hsl(120, 100, 50)) # => green
led_rgb(hsl(240, 100, 50)) # => blue
```
@see https://github.com/python/cpython/blob/3.12/Lib/colorsys.py#L99-L117
'''
_h = h / 360.0
_l = l / 100.0
_s = s / 100.0
if _s == 0.0:
return rgb(int(255 * _l), int(255 * _l), int(255 * _l))
if l <= 0.5:
m2 = _l * (1 + _s)
else:
m2 = _l + _s - (_l * _s)
m1 = 2.0 * _l - m2
return rgb(
int(255 * _v(m1, m2, _h+1/3)),
int(255 * _v(m1, m2, _h)),
int(255 * _v(m1, m2, _h-1/3))
)
def _v(m1, m2, hue):
hue = hue % 1.0
if hue < 1/6:
return m1 + (m2-m1)*hue*6.0
if hue < 0.5:
return m2
if hue < 2/3:
return m1 + (m2-m1)*(2/3-hue)*6.0
return m1
def led_rgb(rgb: int, led: int = ColorLED.ALL, brightness: int = -1):
'''
Control the color LED.
```
led_rgb(Color.RED) # => all to red
led_rgb(Color.RED, ColorLED.L1) # => L1 to red
led_rgb(rgb(255, 10, 30), ColorLED.L1)
# led enumeration:
/L1 R1\\
| ----- |
| maqueen |
| L2 R2 |
```
'''
if _brightness < 2 and brightness < 0:
led_brightness(255)
if brightness < 0:
brightness = _brightness
r = (rgb >> 16) * (brightness / 255)
g = ((rgb >> 8) & 0xFF) * (brightness / 255)
b = ((rgb) & 0xFF) * (brightness / 255)
if led == ColorLED.ALL:
for i in range(4):
_neo_pixel[i] = (int(r), int(g), int(b))
elif led >= 0 and led < ColorLED.ALL:
_neo_pixel[led] = (int(r), int(g), int(b))
_neo_pixel.show()
def led_brightness(brightness: int):
'''
Set the brightness of the color LEDs from 0 to 255.
```
led_brightness(255)
```
'''
global _brightness
if brightness < 0:
brightness = 0
elif brightness > 255:
brightness = 255
_brightness = brightness
def led_rgb_off(led: int = ColorLED.ALL):
'''
Turn off the color LED.
```
led_rgb_off()
led_rgb_off(ColorLED.L1)
```
'''
if led < 0 or led > ColorLED.ALL:
led = ColorLED.ALL
led_rgb(0, led)
# compass tilt compensation: https://ozzmaker.com/compass2/
def mq_heading():
'''
returns the micro:bit heading when mounted on the maqueen [0-360]
```
mq_heading()
```
Tilt Compensation: @see https://ozzmaker.com/compass2/
Axis:
x -> x
z -> -y
y -> z
'''
acc_flat = accelerometer.get_values()
acc_raw = (acc_flat[0], acc_flat[2], -acc_flat[1])
mag_raw = (compass.get_x(), compass.get_z(), -compass.get_y())
acc_norm = sqrt(acc_raw[0] * acc_raw[0] + acc_raw[1] * acc_raw[1] + acc_raw[2] * acc_raw[2])
try:
acc_x_norm = acc_raw[0]/acc_norm
acc_y_norm = acc_raw[1]/acc_norm
pitch = asin(acc_x_norm)
roll = -asin(acc_y_norm / cos(pitch))
mag_x_comp = mag_raw[0] * cos(pitch) + mag_raw[2] * sin(pitch)
mag_y_comp = mag_raw[0] * sin(roll) * sin(pitch) + mag_raw[1] * cos(roll) - mag_raw[2] * sin(roll) * cos(pitch)
heading = 180 * atan2(mag_y_comp, mag_x_comp) / pi
if heading < 0:
heading += 360
return heading
except:
return 0
def heading_set_window_size(n: int = 1):
'''
set the window size for the heading buffer. For calculating the heading_diff, the mean of the last n values is used.
```
heading_set_window_size(5)
```
'''
global _heading_buffer_index
if n < 1:
_heading_window_size = 1
else:
_heading_window_size = n
_heading_buffer.clear()
for i in range(_heading_window_size):
_heading_buffer.append(0)
_heading_buffer_index = 0
def _heading_append(heading: float):
global _heading_buffer_index
_heading_buffer[_heading_buffer_index] = heading
_heading_buffer_index = (_heading_buffer_index + 1) % _heading_window_size
def _heading_mean():
if _heading_window_size == 1:
return _heading_buffer[0]
return sum(_heading_buffer) / _heading_window_size
def heading_diff(heading0: float, apply_window: bool = True):
'''
returns the difference between an initial heading and the current mesaurement
```
h0 = mq_heading()
# maqueen turned 10 degrees to the right
heading_diff(h0) # => 10
```
'''
heading = mq_heading()
if apply_window:
_heading_append(heading)
current = _heading_mean()
else:
current = heading
angle = 180 - abs(abs(heading0 - current) - 180)
if (heading0 + angle) % 360 == current:
return -angle
else:
return angle